Before the introduction of coins, buying or selling of products was done through the barter system .Coins solved the issues associated with the barter system and precious metals were shaped, printed and stamped as a legal method for trading .
The earliest known coins of India were silver punch-marked ones.
- The Indus Valley Civilization –
The civilization may have employed fixed weight metals like silver for trading activity, as evidenced by the DK region of Mohenjo Daro from the late Harappan period (dated 1900–1800 BC or 1750 BC).Based on their extraordinary resemblance and identity between D-class weights, there is a link between Mohenjodaro class IV silver pieces and class D pieces with the Punch marked coins.The striking parallels between Punch-marked currency symbols and those found on Indus seals have also been emphasized.
- Vedic Period Coinage –
All of these units, in some way or another, related to gold cash, but they were eventually used to refer to silver currency.
- The Janapadas & Mahajanapadas(kingdoms of ancient Indian subcontinent) –
The first known Indian coins were silver punch-marked pieces with designs.This ancient Indian coin was minted between 500 and 400 BC by an unnamed prince of Avanti Janapada.It was struck with 3.2 to 3.4 grams of silver and carries the denomination Karshapana.The coins were called Puranas, Karshapanas or Pana.
- Mauryan Empire –
Silver coin was known as Rūpyarūpa
- Satavahana Empire –
Satavahana coins are made of copper, silver, lead, and point and exist in several forms such as round, square, and rectangular.Following Gautamiputra Satakarni, silver coins, the bulk of which bear portraits of Kings, are often discovered.
- Chola Empire –
South Indian numismatists are most familiar with Rajaraja’s coinage. It can be found in tens of thousands. It appears that his coins were the principal currency circulating in Tamil Nadu for numerous centuries. These are both found in gold, silver, and copper.
- The Indo-Greeks –
The Indo-Greeks who acquired control of the subcontinent’s northwest during the second century BCE, were the first to issue coins bearing rulers’ names and images.These coins were made of silver and had images carved into the surface. The coins were usually round (with a few outliers that were rectangular or circular), featured the name of the issuing king as well as depicted legends.
- Kushana Empire –
The North Indian and Central Asian Kushan Empire’s principal coins (about 30–375 CE) were gold coins weighing 7.9 grams and base metal issues weighing 12 grams to 1.5 grams .Although gold was debased with silver in the following centuries, there was little silver currency coined.The coin designs mostly utilize Hellenistic types of image, with a deity on one side and the king on the other, and typically adhere to the styles of preceding Greco-Bactrian emperors in adopting Hellenistic forms of image.
- Vardhana Empire of Kannauj/Taneshwar –
Silver coin was used for financial transactions.
- Gupta Empire –
silver coin was known as Denaree
- The Vijayanagar Empire –
The main coins were made of gold , copper and very few were made of pure silver. “Silver taras” were fractional currency units. These coins inspired the ‘Single Swami’ Pagodas of the Dutch and French and the ‘Three Swami’ Pagodas of the English East India Company.
- Awadh Kingdom –
Gold ashrafi, silver rupee and copper fulus were a part of the monetary system .It is believed that revolutionaries had minted coins in the name of the Nawab-Wazarat .
- Maratha Empire –
Maratha Mints and coinage were consolidated around the middle of the 18th century . Gold , copper and very few silver were used . The coins had the name of Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj minted on them .Three types of Rupees were in circulation:
- Hali Sicca
- Ankushi rupee
- Chandori rupee
- Rajput Kingdoms – The coins of several Rajput lords ruling in Hindustan and Central India were mainly made of gold, copper or billion and very few made of silver. On these coins was the well-known Goddess of riches, Goddess Lakshmi.
- Assam Kingdom – King Chakradhwaja Simha 1663-1670 AD and King Rajeshwar Simha 1751-1769 AD , of Assam Kingdom used Octagonal Silver Rupee (weight 11.3 gram) .
- Tripura Kingdom – King Ratan Manikya II 1695-1712 AD of Tripura Kingdom introduced Silver quarter Rupee (weight 3.8 gram).
- Delhi Sultanate – The gold and silver coins of about 11 grams were introduced and reintroduced.Silver coins were used during Delhi Sultanate.Coins were struck in gold, silver , billon and copper.Tanka was silver and Jital was a copper coin.Chinese inspired paper currency was also introduced but was a failure .
- Sur Empire – Silver coin was known as Rupiya.It was weighing 178 grams.It was equal to 4 copper coins.
- Mughal period – Babur introduced it later modified by Akbar and Shahjahan.Shahrukhi silver coin was introduced by Babur and Jalali, the silver coin was the modified silver coin introduced by Akbar. The legacy of tri-metallism of coinage was started within this period. The silver “rupaiya”, the gold ” mohur” and the copper “tak” were the coins in use during this period.
- British (British India), the French and the Dutch used “Silver” coins and Rupee was made the standard coin – The pagoda was a unit of currency, a coin made of gold or half-gold minted by Indian dynasties as well as the British, the French and the Dutch. It was subdivided into 42 fanams. The pagoda was issued by various dynasties in medieval southern India, including the Kadambas of Hangal, the Kadambas of Goa, and the Vijayanagara Empire.
The French struck local gold “pagodas” and silver “fanams” under contract by the nawabs. The silver coins of the French were called “fanon” which were equivalent to the local “fanam” and could be exchanged at the rate of 26 fanon to one gold pagoda. The Indian rulers paid their arrears to the French, English and other European East India Companies in Pagodas.
The ‘swami’ gold pagodas were issued by the British East India Company (E.I.C.) between 1740 and 1807.In 1807 new machinery was introduced and mint produced 2 silver coin in European style with oblique milling. One series based on Hindu standard consisted of One and Two pagoda in gold, Half and Quarter pagoda and Fanams in silver.They issued rupees together with fractions down to ⅛ and 1⁄16 rupee in silver. After 1818, Rupee was made the standard coin and the weight was fixed at 180 grains with smaller pieces in proportion. The pagodas and fanams were demonetized from that year. In 1835, the East India Company unified all the coinage under the Coinage Act and the new coins minted in 1835 had the effigy of William IV on the obverse and the value on the reverse in English and Persian.
Further , king George VI replaced the native designs on banknotes and coins but after the revolt of 1857, he made the Rupee as the official currency of colonial India. In the honour of Queen Victoria in 1862, series of bank notes and coins were issued with the Victoria portrait. The Paper Currency Act of 1861 gave the Government the monopoly of note issued throughout the vast expanse of British India.
During the British East India Company i.e. 1600, The Mughal currency remained popular but in 1717 AD, Farrukh Siyar the Mughal Emperor gave permission to the Britishers or the English to coin Mughal money at the Bombay mint. Then British gold coins were termed as Carolina, the silver coins as Angelina, the copper coins as cupperoon and the tin coins as tinny.
In the 18th Century, the Bank of Hindostan General Bank in Bengal and the Bengal Bank became the first banks in India to issue paper currency i.e. during this time paper money was first issued in British India.
With “the Coinage Act of 1835” and “the Paper Currency Act of 1861” , uniform coinage throughout the country comes. And in 1858, Mughal empire subsequently ended and British crown gained control over one hundred princely states and so, the images on the coins were replaced by portraits of the Monarch of Great Britain Supremacy.
Rupee was/is the common name for the currencies of India, Indonesia, the Maldives, Mauritius, Nepal, Pakistan, Seychelles, and Sri Lanka, and of former currency system of Afghanistan, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, the UAE (as the Gulf rupee), British East Africa, Burma, German East Africa (as Rupie/Rupien), and Tibet. In Indonesia and the Maldives the unit of currency is known as rupiah and rufiyaa respectively. The Indian rupees (₹) and Pakistani rupees (₨) are subdivided into 100 paise. The Mauritian, Seychellois, and Sri Lankan rupees subdivide into 100 cents. The Nepalese rupee subdivides into 100 paisa.
Note : Most importantly, the word Rupee word had its journey from Sanskrit word (Indian language) stolen by muslims and later by christians as mentioned below :

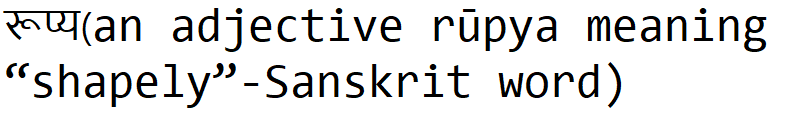

finally we hear “Rupee”
After gaining Independence in 1947 and in 1950s when India become Republic, India’s modern Rupee reverted back to the design of signature Rupee coin. The symbol chosen for the paper currency was the Lion capital at Sarnath which replaced the George VI series of bank notes. So, the first banknote printed by the Independent India was a 1 rupee note.
Do you know the history of 1 rupee note ?
One rupee note was issued on 30 November,1917 under the British Raj. During the first world war British domination was there. At that time one rupee coin was a silver coin. But because of the war, condition became worse and one rupee coin of silver was not able to generate. And due to this first time in front of people one rupee note issued and the image of George V was inbuilt in the note. Printed in England this one rupee note value was very less as compared to others.
Why Indians are not aware of India , Indians , Indian Civilization/Culture ?
I guess the reason for this is more to do with the way we Indians have been brought up. The Macaulian education system further with the leftist marxist historians leaning towards the fake one-sided selective Nehruvian Secularism has always omitted the Historical Indian Genius and Greats showing Indians as a defeated race with nothing to be proud of. In short in poor light.
May be this is the mind set of slavery wherein islamic foreign invader like Mughal Akbar who was a ruthless ruler who slaughtered more than 30000 unarmed peasants inside the Chittaur Fort in 5 days, who had a HAREM of more than 3000 Hindu women, who destroyed several Hindu temples in Daob region between Ganga and Yamuna region or Kalika temple at Chittaur etc to name a few is called GREAT. Irony dies 1000 times when we call him secular. The right word is he was Tactical and interested only in expansion of his empire and Islam.
The same mind set of slavery goes for christians foreign invaders (like britishers,portuguese,etc) who were only interested only in expansion of the empire and christianity .
Therefore , “silver” metal and word “Rupee” has a great history not only in India but across the entire world but due to the Macaulian education system along with the leftist marxist historians leaning towards the fake one-sided selective Nehruvian Secularism Indians are not aware about the true history , true glory and true greatness of India and Indians .
“BUT IRONY IS THAT PEOPLE ARE REJECTING , NEGLECTING , MISUNDERSTANDING AND INSULTING THEIR OWN ROOTS , OWN ANCESTORS/ANCESTRESSES , OWN PREDECCESORS , OWN CULTURE AND ACCEPTING CULTURES/RELIGIONS OF THE FOREIGN INVADERS DIRECTLY AND INDIRECTLY .
RELIGIONS/CULTURES OF MORE THAN 150 COUNTRIES WERE / ARE DESTROYED BY THE TWO ABRAHAMIC RELIGIONS NAMELY islam and christianity (VIA VIOLENCE AND CHEATING)”.
